There are many known causes when the desire to have children is unfulfilled despite unprotected intercourse. One reason may be a lack of ovulation, which is also known by the medical term “Anovulation”. If this is the cause, it is good to know that PROFERTIL® female can support ovulation.
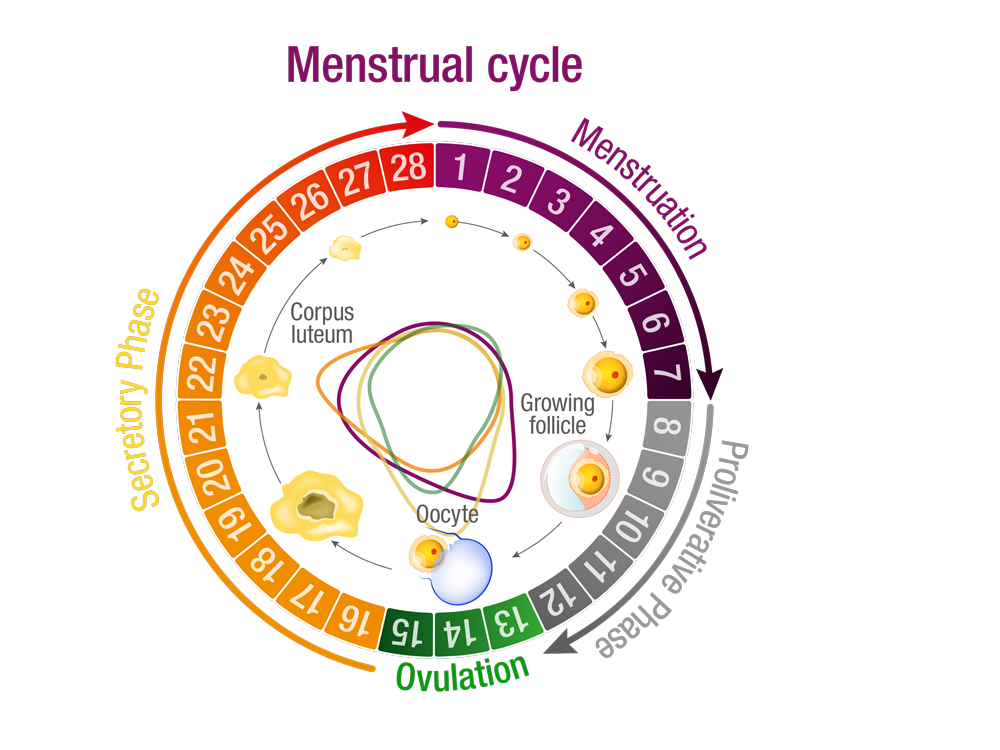
The egg cell is located in a mature follicle (ovarian follicle) and the maximum size of the follicle will be reached towards the middle of the cycle. Then the follicle opens and the egg cell is released with the liquid. This is the process of ovulation. The egg cell is transported via the fallopian tubes to the uterus in the next step after ovulation.
The first half of the female cycle is oestrogen dominated. This hormone influences the maturation of the egg cell in the ovary. Ovulation on the 14th day in the daily cycle initiates the second half of the cycle.
What is oestradiol?
Oestradiol is a sex hormone primarily produced in the ovarian follicles.
The woman’s oestradiol values are cycle-dependent. The concentration in the blood serum is 25 to 95 ng/l in the first half of the cycle. It lies between 75 and 570 ng/l in the ovulation period. The value drops to between 60 ng/l and 250 ng/l in the second half of the cycle. The value drops to less than 45 ng/l in post-menopause, i.e. after menopause.
Chronic anovulation, which is a disturbance in the cycle with a lack of ovulation, is considered to be a common cause of female infertility. It should also be noted that a lack of ovulation is usually the result of hormonal imbalance. If ovulation is too infrequent or non-existent, a polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be present. But for a diagnosis to be made, two of the three Rotterdam criteria must be met.

What actually are menstrual disorders?
Regular menstruation is also called “eumenorrhoea”. Deviations are referred to as cycle disorders that influence the period intensity or the interval between periods.
Interval changes can have the following forms:
- Primary/secondary amenorrhoea (first menstrual period has not begun/menstrual periods absent after previously existing)
- Oligomenorrhoea (more than 35 days between two menstrual periods)
- Polymenorrhoea (less than 25 days between two menstrual periods)
- Hypomenorrhoea (weak menstruation)
- Dysmenorrhoea (painful menstruation/menstrual pain)
- Menorrhagia (heavy and long-lasting menstrual period)
- Metrorrhagia/intermenstrual bleeding (acyclic menstrual period outside the normal menstrual cycle)
Poor egg cell quality as a cause for irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation
With regard to the supply of nutrients to increase female fertility, micronutrients have an important role to play. This is particularly true for a polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PROFERTIL® female can meet this need to help the female body to improve the egg cell quality and encourage ovulation.
A clinical study with PCOS patients showed that PROFERTIL® female results in the harmonisation of PCOS-specific, hormonal parameters (e.g. testosterone) after taking for a 3-month period.
Let’s clarify the question of what is meant by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS):
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disease that occurs in childbearing age. It is one of the most common causes for the unfulfilled desire to have children in women. The disruption of egg cell maturation is possible.
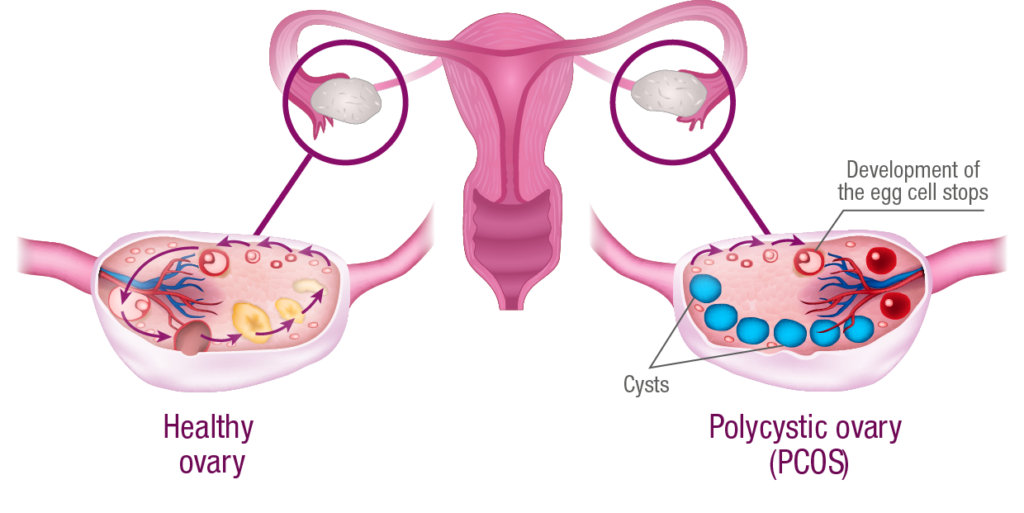
According to the Rotterdam criteria, the characteristic PCOS symptoms include:
- Chronic cycle disorders, especially oligomenorrhoea (longer cycles) or amenorrhoea (the complete absence of the menstrual period) with a lack of ovulation (anovulation)
- Excessive male sex hormone (hyperandrogenism) with the possible development of female facial hair, loss of hair on the scalp and the formation of acne
- Multiple cyst formation on the ovaries
The following points may indicate PCOS:
- Unfulfilled desire to have children
- Increased blood fat values
- Disturbed sugar metabolism (insulin resistance) though to diabetes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Increased level of Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
Therapy options for PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can be relieved with the right therapies and often also a change in lifestyle, which includes possibly required weight loss. Regular physical exercise is important because it can stabilise the hormone balance as well as sugar metabolism.
In case of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and the desire to have children, the treatment can be adapted accordingly if required. In this context, again reference should be made to the study-proven formulation of PROFERTIL® female, which provides targeted support for cycle disorders. Medication to stimulate the ovaries can be another option. A medical study has confirmed that PROFERTIL® female demonstrably contributes to the hormone balance in PCOS patients.
Furthermore, PROFERTIL® female optimally prepares the body for pregnancy with a carefully selected combination of micronutrients.
A medical study has confirmed that PROFERTIL® female demonstrably contributes to the hormone balance in PCOS patients. Furthermore, PROFERTIL® female optimally prepares the body for pregnancy with a carefully selected combination of micronutrients.

What else can be responsible for a cycle disorder?
Organic causes
- Formation of fibroids or polyps
- Endometriosis (cysts and inflammation e.g. of the ovaries)
- Endometrial hyperplasia (excessive growth of the uterine lining)
- Cancer of the uterus
Hormonal causes
- Lack of ovulation (anovulation)
- High prolactin levels (prolactin stimulates milk production in the breast)
- Increased production of oestrogens (oestrogens = female sex hormones)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid dysfunction
Blood clotting disorder
- Thrombocytopenia (blood platelet count is too low)
- Increased fibrinolysis (increased fibrin separation; Fibrin = Plasmatic blood clotting adhesive)
- Von Willebrand disease (blood clotting disease)
Influencing medications
Oestrogens, heparin, coumarin, tamoxifen
Other influencing factors:
- Psychological stress
- Various general diseases
- Poor nutritional habits
- Competitive sport
- The intrauterine device (IUD) and the pill
How is a cycle disorder diagnosed?
Following a detailed anamnesis, organic causes are ruled out first. A multi-month cycle calendar can be helpful. This should document frequency and intensity. These recordings should be supplemented by a gynaecological examination with ultrasound. Laboratory analyses provide information about any possible hormone disorders.
What can be done for a diagnosed cycle disorder?
In this respect, support of ovulation, an improvement of egg cell quality or an increase in the number of mature egg cells are essential. The regulation of the hormonal balance (e.g. a lowering of increased testosterone levels) is also important. The study-proven composition of PROFERTIL® female can improve the conditions for a regular cycle.
Why PROFERTIL® female?
Despite regular intercourse without protection, around 15% of couples remain involuntarily unable to have children. The cause is roughly equally weighted between the woman, i.e. the “Female factor”, and the man, where the term “Male factor” is used. There can also be a combination of both factors.
It is a fact that many women or couples over the age of 30 or even 40 want to fulfil their desire to have children. However, the egg cell quality is then already reduced and the cycle may well be irregular. Cycle disorders are more common. Fertility ultimately decreases with age.
The intake of PROFERTIL® female can help here. The study-proven micronutrient formulation demonstrably supports female fertility.



